Introduction to Cloud Data Warehousing
Leveraging the capabilities of present-day cloud structure as an Ultimate step, many databases, Marketing applications, and ERPs have been migrated to the cloud.
Consequently, nearly all files and records of value to a company are now stored in the cloud.
Thus, companies need a data warehouse to store the data received from cloud-based applications.
Therefore, this is where the Cloud Data Warehouse comes into the picture.
Large amounts of data must be handled and analyzed in various companies and data-driven businesses, necessitating robust solutions for the same.
What is Cloud Data Warehousing?
Key Components and Architecture
Data Storage: Data warehouses keep a much more virtually unlimited amount of cloud storage. It can capture data of different structures such as structured data, semi-structured data, or unstructured data meaning that all crucial data can be stored in one place.
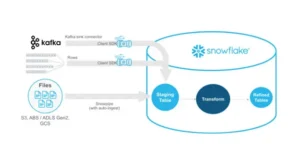
Data Integration: Data is pulled from different sources, which may range from transactional databases, applications, and external data sources to the cloud data warehouse. The ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) and ELT (Extract, Load, Transform) methodologies are well-known instruments for maintaining data consistency and data quality.
Query Processing: Robust query processing engines can provide efficient and faster responses to data searches. Cloud data warehouses use MPP (massively parallel processing) to divide query loads into several nodes hence enhancing performance and speed.
Analytics and BI Tools: Modern cloud data warehouses are intended to integrate with analytics and business intelligence solutions. This integration enables users to generate data-driven insights, create visuals, and conduct advanced analytics on the data stored in the warehouse.
Benefits of Cloud Data Warehousing
Scalability: One of the major strengths of cloud data warehousing is the quick capability of scalability particularly due to rapid business expansion. They can dynamically adjust storage and compute capacity as needed, ensuring the required level of performance without over-provisioning.
Cost-Effectiveness: Cloud data warehousing works on the dynamic charging structure which means an organization pays only for what it uses. This does away with hefty capital investments on the hardware and software, making this a very compelling proposition for any organization. Many businesses are even adopting offshore data warehousing models to further enhance cost efficiency while leveraging global talent for data operations.
Flexibility: Cloud data warehouses are versatile, as they support all forms of data from almost any source; this makes integration of data sets possible. It is indeed important for contemporary data analytics operations which tend to involve data from many sources to generate comprehensive insights and make informed decisions.
Performance: With MPP architecture and complex query processing engines, CDW delivers high performance even for heavy queries and big datasets. This results in real-time analytics for the business and greater decision-making capabilities.
Accessibility: The data stored in the cloud data warehouses is readily available to users from any location, which assists the working of distributed teams. This accessibility is very beneficial in nowadays’ remote and hybrid work settings.
Significance in Modern Data Analytics Workflows

- Enhanced Data Integration: Cloud data warehouses enhance data integration from different sources. This integration is critical in presenting a holistic view of the organization’s data to enable accurate analysis of the data and information generated.
- Real-Time Analytics: Cloud data warehouses can operate in real-time because of their ability to process a lot of data at once or address complex queries. This enables organizations to adapt to dynamic market conditions and customer requirements with a lot of ease.
- Advanced Analytics Capabilities: Cloud data warehouses can accommodate high-level analysis techniques like machine learning and Artificial Intelligence. These capabilities facilitate organizations in gaining deeper insights and drive innovation.
- Improved Collaboration: Easy accessibility and centralization of cloud data warehousing brings together data scientists, analysts, and business users and ensures collaboration. This collaboration is vital in developing and implementing data-driven strategies.
- Cost Efficiency: The consumers get charged based on their usage of the cloud services, aka pay-as-you-go pricing, and there is a minimal investment in the hardware and software, which make up the lower total cost of the ownership. This has led to affordability in ways that allow different forms of data analytics to be embraced across different organizations without being restricted to large institutions and corporate organizations only but also the smaller organizations within the marketplace place, such as small and medium enterprises.
- Data Governance and Security: Data governance and security in cloud data warehouses are well managed to ensure that the data is secure and meets regulatory standards. This is important to keep clients on board and ensure data security and compliance with the law.
Future Trends and Development
- Integration with AI and Machine Learning: There will be an active blending of AI and machine learning with cloud data warehousing. This will allow more advanced data analysis and predictive modeling, driving innovation across industries.
- Hybrid and Multi-Cloud Strategies: The companies will continue leveraging hybrid and multi-cloud strategies, combining on-premises, private cloud, and public cloud resources. These strategies will rely on cloud data warehouses as they will play a pivotal role by providing flexibility to manage and analyze data across different settings.
- Edge Computing: The new trend of edge computing will augment cloud data warehousing by enabling data processing closer to the source This will minimize the latency and enable real-time analytics in areas like IoT and autonomous vehicles.
- Enhanced Data Security and Privacy: Hence there will still be improvements in security and compliance as the data privacy laws become strict across the world. This will assist the organizations in the protection of sensitive data and also meet the regulatory requirements.
Conclusion
Cloud data warehousing is revolutionizing the way data is collected, stored, and analyzed by different companies.
Building on such industry features as scalability, flexibility, and cost efficiency of the cloud infrastructure, enterprises can consolidate various large data sets, perform real-time data analytics, and gain deeper business insights. When combined with offshore data warehousing strategies, organizations can unlock further advantages by accessing global infrastructure and talent pools while ensuring round-the-clock operations and cost optimization.
The concept of cloud data warehousing will continue to evolve as it becomes the cornerstone of modern data analytics workflows, driving innovation and enabling data-driven decision-making across industries.
If you’re ready to embark on this journey and need expert guidance, subscribe to our newsletter for more tips and insights, or contact us at Offsoar to learn how we can help you build a scalable data analytics pipeline that drives business success. Let’s work together to turn data into actionable insights and create a brighter future for your organization.

How LLMs Are Revolutionizing Text Mining and Data Extraction from Unstructured Data
Leveraging LLMs for Advanced Text Mining and Data Extraction from Unstructured Data Since digital transformation is growing exponentially, businesses generate huge amounts of unstructured data from sources like emails, PDFs,

How Businesses Use LLMs for Competitive Intelligence to Stay Ahead of the Curve
How Businesses Use LLM’s for Data-Driven Competitive Intelligence to stay ahead of the curve Competitive intelligence (CI) is essential for keeping a competitive edge in today’s fast-paced business world. Businesses

Maximizing Cost-Efficient Performance: Best Practices for Scaling Data Warehouses in Snowflake
Maximizing Cost-Efficient Performance: Best Practices for Scaling Data Warehouses in Snowflake Organizations rely on comprehensive data warehouse solutions to manage substantial volumes of data while ensuring efficiency and scalability. Snowflake,

Comprehensive Guide to Implementing Effective Data Governance in Snowflake
Mastering Data Governance with Snowflake: A Comprehensive Guide Data governance is a systematic way to manage, organize, and control data assets inside an organization. This includes developing norms and policies
Efficiently Managing Dynamic Tables in Snowflake for Real-Time Data and Low-Latency Analytics
Managing Dynamic Tables in Snowflake: Handling Real-Time Data Updates and Low-Latency Analytics In this data-driven environment, businesses aim to use the potential of real-time information. Snowflake’s dynamic tables stand out

Mastering Data Lineage and Traceability in Snowflake for Better Compliance and Data Quality
Mastering Data Lineage and Traceability in Snowflake for Better Compliance and Data Quality In data-driven businesses, comprehending the source, flow, and alterations of data is essential. Data lineage is essential



