
Comprehensive Guide to Implementing Effective Data Governance in Snowflake
Mastering Data Governance with Snowflake: A Comprehensive Guide
What is Snowflake Data Governance?
Overview of built-in Snowflake governance features
Column-Level Security
Column-level security, available in Snowflake Enterprise edition or higher, safeguards sensitive data in table or view columns. This includes:
- Dynamic Data Masking: Masking restrictions are applied at query runtime to ensure that unauthorized users only see obfuscated data while authorized users can access plain-text data.
- External Tokenization: External services are used to tokenize data before putting it into Snowflake, and then it is detokenized dynamically during query execution.
Masking Policies are schema-level objects that define criteria and functions to secure sensitive data while limiting access to authorized users.
-- Dynamic Data Masking
CREATE MASKING POLICY employee_ssn_mask AS (val string) RETURNS string ->
CASE
WHEN CURRENT_ROLE() IN ('PAYROLL') THEN val
ELSE '******'
END;
-- External Tokenization
CREATE MASKING POLICY employee_ssn_detokenize AS (val string) RETURNS string ->
CASE
WHEN CURRENT_ROLE() IN ('PAYROLL') THEN ssn_unprotect(VAL)
ELSE val -- sees tokenized data
END;
Row-Level Security
Object Tagging
Object tagging makes data management easier by allowing users to add metadata tags to Snowflake objects like tables and schemas. Tags are key-value pairs that allow for efficient data classification, tracking of sensitive data, and the implementation of tag-based access rules.
For example:
Create a tag named cost_center with ‘finance’ and ‘engineering’ as the only two allowed string values:
create tag cost_center
allowed_values 'finance', 'engineering';
Verify the allowed values:
select get_ddl('tag', 'cost_center')
+------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| GET_DDL('tag', 'cost_center') |
|------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
| create or replace tag cost_center allowed_values = 'finance', 'engineering'; |
+------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
Modify the tag named cost_center to add ‘marketing’ as an allowed string value:
alter tag cost_center
add allowed_values 'marketing';
Modify the tag named cost_center to drop ‘engineering’ as an allowed string value:
alter tag cost_center
drop allowed_values 'engineering';
To obtain the list of allowed string values for a given tag, call either the GET_DDL function or the SYSTEM$GET_TAG_ALLOWED_VALUES function. For example, assuming that the tag cost_center is stored in a database named governance and a schema named tags:
select system$get_tag_allowed_values('governance.tags.cost_center');
+--------------------------------------------------------------+
| SYSTEM$GET_TAG_ALLOWED_VALUES('GOVERNANCE.TAGS.COST_CENTER') |
|--------------------------------------------------------------|
| ["finance","marketing"] |
+--------------------------------------------------------------+
Tag-based Masking Policies
Masking policies are automatically applied to columns depending on their associated tags. This feature provides consistent protection across tagged columns, avoiding the need for manual policy assignments. It works neatly with column data types and prefers explicitly assigned masking policies to tag-based ones.
Data Classification
Object Dependencies
Object dependencies let users to trace links between Snowflake objects, thereby aiding impact analysis, data integrity, and regulatory compliance. This functionality is very useful for compliance officials who need to trace data back to its source.
Access History
The access history feature records every user activity involving data access and modification, including queries and SQL statements. It helps with regulatory compliance auditing, providing insights into frequently accessed data, and is accessible through the Account Usage ACCESS_HISTORY view.
Managing Access in Snowflake
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
Snowflake’s RBAC ensures secure and organized access management by allocating roles and rights to user accounts. Roles (representing user groups), privileges (defining activities like SELECT or INSERT), and grants (which connect roles to privileges) are all important components. For example:
-- Create a role
CREATE ROLE healthcare_data_analyst;
-- Grant privileges to the role
GRANT SELECT ON DATABASE patient_data TO ROLE healthcare_data_analyst;
-- Assign role to a user
GRANT ROLE healthcare_data_analyst TO USER jane_doe;
This configuration guarantees that only authorized users have access to specified datasets, hence improving security and compliance.
Fine-Grained Access Control
-- Create a masking policy
CREATE MASKING POLICY ssn_mask AS
(val STRING) RETURNS STRING ->
CASE
WHEN CURRENT_ROLE() IN ('data_admin') THEN val
ELSE 'XXX-XX-XXXX'
END;
-- Apply the policy to a column
ALTER TABLE patient_data ADD MASKING POLICY ssn_mask ON ssn;
This policy ensures that sensitive information, such as social security numbers, stays confidential for unauthorized users while providing secure access to others.
Tracking Audit Trails in Snowflake
Importance of Audit Trails
Audit trails are critical for complying with standards such as HIPAA and GDPR because they record who accessed data, when, and how. They assist organizations in maintaining accountability, detecting unwanted access, and meeting reporting obligations. Typical audit requirements include monitoring query logs and spotting trends of sensitive data access.
-- Cluster the dynamic table on frequently queried columns
ALTER TABLE dynamic_table
CLUSTER BY (update_time, id);
Snowflake’s Query History and Access Logs
SELECT QUERY_TEXT, USER_NAME, START_TIME, END_TIME
FROM TABLE(INFORMATION_SCHEMA.QUERY_HISTORY())
WHERE USER_NAME = 'jane_doe'
AND START_TIME >= '2025-01-01 00:00:00';
Integrating Audit Data with External Tools
Best Practices for Implementing Snowflake Data Governance
Leverage Snowflake’s Built-in Features.
Snowflake’s governance solutions, like object tagging, dynamic data masking, row access controls, and object dependencies, can help you properly classify, secure, and audit data.
Define Data Policies and Procedures.
Create explicit policies on data quality, privacy, security, retention, and access. Regularly evaluate and update these policies to ensure their relevance and effectiveness.
Form a Dedicated Governance Team.
Form a Governance Council/Committee with specific functions, such as data stewards, managers, custodians, compliance officers, and data architects. Many organizations also hire data governance experts to advise on complex regulatory requirements or accelerate the rollout of governance frameworks. This team enforces governance procedures that are matched with business requirements.
Develop a Governance Framework.
Implement a structured framework of rules, procedures, guidelines, and standards to ensure uniform data governance throughout the firm. Include escalation procedures for governance issues.
Ensure Robust Security Measures.
Implement security mechanisms such as access restriction, encryption, and data masking. Monitoring and incident response processes must be established to address security breaches as soon as possible.
Maintain High Data Quality Standards.
Implement validation, cleansing, and enrichment processes to assure data correctness, consistency, and reliability.
Utilize Automation and Monitoring Tools.
Set up tools to automate classification and enforce policies. Use monitoring technologies to track user access, detect security problems, and ensure data quality.
Conclusion
Implementing effective data governance in Snowflake is critical for guaranteeing data security, compliance, and dependability in today’s data-driven environment. Organizations can streamline data management by using Snowflake’s built-in governance tools, developing strong policies, forming a dedicated governance team, and implementing an organized framework. Implementing strong security measures, upholding data quality standards, and utilizing automation and monitoring tools improve governance procedures. A well-executed Snowflake data governance policy safeguards sensitive data and enables businesses to make educated decisions, build trust, and generate long-term success. Whether you build internal capabilities or hire data governance experts for specialized support, begin developing a durable data governance model immediately to realize Snowflake’s full potential.
If you’re ready to embark on this journey and need expert guidance, subscribe to our newsletter for more tips and insights, or contact us at Offsoar to learn how we can help you build a scalable data analytics pipeline that drives business success. Let’s work together to turn data into actionable insights and create a brighter future for your organization.

How LLMs Are Revolutionizing Text Mining and Data Extraction from Unstructured Data
Leveraging LLMs for Advanced Text Mining and Data Extraction from Unstructured Data Since digital transformation is growing exponentially, businesses generate huge amounts of unstructured data from sources like emails, PDFs,

How Businesses Use LLMs for Competitive Intelligence to Stay Ahead of the Curve
How Businesses Use LLM’s for Data-Driven Competitive Intelligence to stay ahead of the curve Competitive intelligence (CI) is essential for keeping a competitive edge in today’s fast-paced business world. Businesses

Maximizing Cost-Efficient Performance: Best Practices for Scaling Data Warehouses in Snowflake
Maximizing Cost-Efficient Performance: Best Practices for Scaling Data Warehouses in Snowflake Organizations rely on comprehensive data warehouse solutions to manage substantial volumes of data while ensuring efficiency and scalability. Snowflake,

Comprehensive Guide to Implementing Effective Data Governance in Snowflake
Mastering Data Governance with Snowflake: A Comprehensive Guide Data governance is a systematic way to manage, organize, and control data assets inside an organization. This includes developing norms and policies
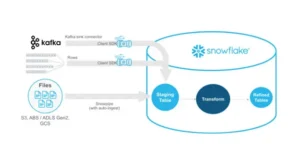
Efficiently Managing Dynamic Tables in Snowflake for Real-Time Data and Low-Latency Analytics
Managing Dynamic Tables in Snowflake: Handling Real-Time Data Updates and Low-Latency Analytics In this data-driven environment, businesses aim to use the potential of real-time information. Snowflake’s dynamic tables stand out

Mastering Data Lineage and Traceability in Snowflake for Better Compliance and Data Quality
Mastering Data Lineage and Traceability in Snowflake for Better Compliance and Data Quality In data-driven businesses, comprehending the source, flow, and alterations of data is essential. Data lineage is essential
